Understanding Click Fraud: The Dark Side of E-Commerce in Kenya
In the ever-evolving world of e-commerce, businesses strive to attract attention, drive traffic, and convert visitors into customers. However, as competition intensifies, some entities resort to unethical practices to gain an unfair advantage. One such practice is “click fraud,” a deceptive tactic that manipulates the digital marketplace. In this article, we delve into what click fraud is, how it works, the risks it poses, and the tactics used by those involved.
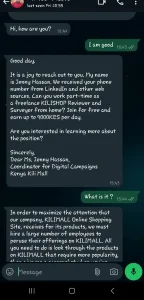
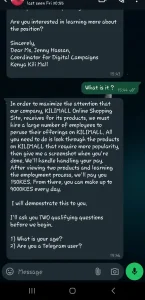
Below is are screenshots of a person trying to recruit a Kenyan to do Click Fraud. The person was first Contacted on Linkedin before the conversation moved into WhatsApp. Once you receive a small stipend of 150 Ksh, you are required to join an Exclusive Telegram Group where recruits are given tasks on a daily basis.
What is Click Fraud?
Click fraud is the act of generating fraudulent clicks on digital advertisements, product pages, or website links to create the illusion of higher engagement. This practice is often driven by agencies or individuals who aim to manipulate metrics such as search engine rankings, product popularity, or website traffic. The goal is to deceive algorithms, advertisers, and consumers, making it appear that a product or service is more popular than it actually is.
How Click Fraud Works
- The Role of Agencies and Businesses:
- Agencies: Some marketing agencies or unscrupulous businesses engage in click fraud to boost their clients’ online presence. They either carry out these activities themselves or outsource them to individuals who are paid to generate clicks.
- Businesses: Certain companies may employ click fraud tactics to outshine competitors or artificially inflate their market presence.
- Recruitment of Clickers:
- Incentives: Individuals, often found through online job platforms or social media groups, are offered small payments for each click they generate. Payments are typically made through cash transfers, mobile money, or digital wallets.
- Target Audience: The practice is particularly prevalent in regions with high unemployment rates, where the promise of quick, easy money is highly attractive.
- The Process:
- Participants are directed to click on specific product pages or ads multiple times, inflating the click count.
- The increased clicks can lead to higher rankings within e-commerce platforms, improved ad visibility, or a false impression of product popularity.
Tactics Used in Click Fraud
Click fraud schemes can vary in complexity, ranging from simple manual clicking to more sophisticated methods:
- Manual Click Fraud:
- Individuals are paid to manually click on product pages or ads. This method is labor-intensive but can be scaled up by recruiting large numbers of people.
- Botnets:
- In more advanced schemes, botnets (networks of infected computers) are used to generate thousands of clicks automatically. These clicks can be programmed to mimic human behavior, making detection more difficult.
- Click Farms:
- Click farms are operations where large groups of people are hired to click on links, often working from a centralized location. These farms can generate massive volumes of fraudulent clicks, further skewing metrics.
- Proxy Networks:
- Fraudsters may use proxy servers to mask the origin of clicks, making it appear as though the traffic is coming from various legitimate sources.
Risks and Consequences of Click Fraud
While click fraud may seem like an easy way to boost online metrics, it carries significant risks for all parties involved:
- For E-commerce Platforms:
- Data Integrity: Click fraud distorts data, leading to inaccurate insights into customer behavior and product performance.
- Algorithm Manipulation: Fraudulent clicks can skew search engine and platform algorithms, unfairly promoting certain products or services.
- Platform Reputation: If e-commerce platforms become known for allowing fraudulent activities, their reputation can suffer, leading to a loss of trust among users.
- For Businesses:
- Penalties: E-commerce platforms may penalize businesses caught engaging in click fraud by suspending or banning their accounts.
- Legal Repercussions: In some jurisdictions, click fraud is illegal, and businesses can face fines or other legal consequences.
- Long-term Impact: While click fraud may offer short-term gains, it can damage a brand’s reputation and erode consumer trust in the long run.
- For Individuals:
- Ethical Concerns: Participating in click fraud is dishonest and can contribute to broader issues of online fraud and corruption.
- Legal Risks: Individuals involved in click fraud may also face legal consequences, depending on the laws in their country.
- Financial Impact: The small payments offered for click fraud participation may not be worth the potential risks, including being caught in a legal investigation.
The Scope of Click Fraud in Kenya
In Kenya, click fraud is becoming an increasingly prevalent issue, driven by several factors:
- Economic Pressure:
- High unemployment rates and economic challenges make click fraud an attractive option for many Kenyans seeking quick income.
- Accessibility of the Internet:
- The widespread availability of the internet in Kenya allows easy access to click fraud opportunities, with many people recruited through social media and online job platforms.
- Regulatory Challenges:
- The rapid growth of the digital economy in Kenya has outpaced the development of regulatory frameworks, making it difficult to combat click fraud effectively.
Combating Click Fraud: What Can Be Done?
To address the issue of click fraud, several measures can be taken by various stakeholders:
- For E-commerce Platforms:
- Advanced Detection Tools: Investing in sophisticated fraud detection tools that can identify and block fraudulent clicks in real time.
- User Education: Educating sellers and consumers about the dangers of click fraud and promoting ethical practices within the platform.
- Stronger Regulations: Working with regulators to establish clearer guidelines and consequences for those caught engaging in click fraud.
- For Businesses:
- Avoiding Unethical Practices: Focusing on legitimate marketing strategies and avoiding the temptation of short-term gains through click fraud.
- Transparency: Being transparent with customers about marketing practices and building trust through ethical behavior.
- For Individuals:
- Awareness: Understanding the risks and ethical implications of participating in click fraud.
- Alternative Opportunities: Seeking out legitimate online work opportunities that provide sustainable income without the associated risks.
Conclusion
Click fraud is a significant challenge in the digital marketplace, with far-reaching consequences for e-commerce platforms, businesses, and individuals alike. In Kenya, the practice is on the rise, driven by economic pressures and the allure of easy money. However, the risks involved—from legal repercussions to damage to reputations—far outweigh the short-term benefits. Combating click fraud requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders, including stronger regulations, better detection methods, and increased awareness of the ethical and legal implications of such practices. By working together, we can create a more transparent and trustworthy digital marketplace for all.